Aircada Has Evolved
We have officially retired our industrial software to focus entirely on the future of retail: interactive 3D product configurators.
Why You Were Redirected Here
If you clicked a link looking for Aircada Pro, our old augmented reality articles, or industrial SCADA comparisons, you are in the right place.
After years of building complex data overlays for factory floors, we made the strategic decision to sunset our industrial manufacturing tools. We realized our core rendering technology could solve a massive problem in a completely different industry. We took everything we learned about building lightning-fast, web-based 3D engines and pivoted entirely to e-commerce.
The New Aircada: 3D E-Commerce Configurators
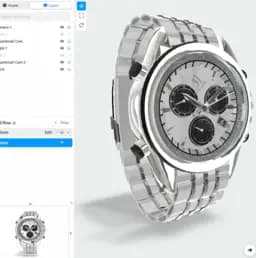
Today, Aircada is solely dedicated to building premium 3D product configurators for online brands. We've helped large retailers like mountainFLOW from Shark Tank, American Pickleball League, Cinch Gaming, and many more replace their static product photos with interactive 3D configurators, increasing conversions along the way. Our tools are designed to be easy to integrate, WebGPU fast, and optimized for mobile browsers. So far so good.
Explore Our New Platform
- 3D Product Configurators →
Discover our core WebGPU rendering engine built specifically for high-performance e-commerce.
- Shopify 3D Product Configurator →
Learn how to seamlessly integrate our 3D customization studio directly into your Shopify storefront.
- Book a 3D Configurator Demo →
Schedule a personalized walkthrough of our platform and see how we can increase your conversion rates.
- E-Commerce 3D Case Study: mountainFLOW →
Read how leading brands use our 3D tools to increase customer engagement and drive online sales.
- 3D Configurator Pricing →
View our transparent, flat-rate pricing plans designed to scale with your growing business.